名詞定義: 熱力學thermodynamics, 源自十九世紀工業革命, engine可以把熱能轉換成機械能,如何100%轉換辦不到,轉而研究如何高效轉換!機械系研究主題之一
甚麼東西決定自然界事物的行為變化? 以能量觀點解釋
熱力學的重點: 1. 計算能量的變化(狀態之間的變化), heat capacity→求T, P e.g. 結晶材料中空位的平衡濃度,雜質的溶解度 2. 尋找某種環境條件的平衡態
巨觀上探討即是古典熱力學;微觀上從粒子(原子,分子,電子)行為表現出巨觀的變化,探討統計熱力學: 粒子的分布機率去解釋內能,熵的熱力名詞
thermodynamics in material, in terms of component(element, compound)
one component(unary) binary, ternary, quaterary(multi-component)
homogeneous hetrogeneous
closed system open system
non-reacting reacting
simple system(Q,W,H,U...) complex system(ℰ,ℳ,Opt...)
thermodynamic variables操作的變數: T, P, V, nᵢ, U, H, S, A, G
→ 可以是狀態函數Z的變數, state 1 →→ state 2 ∆Z=Z₂-Z₁
數學上稱狀態函數和變數,與路徑無關, state function: T, P, V, nᵢ, U, H, S, A, G ∆Z=∫₁²dz
process variable: Q, W 與路徑有關 ΔZ=??=∫ₚₐₜₕδZ
state 1 →→ state 2 ∆Z=Z₂-Z₁=∫₁²dz, ∮dz=0 cycle.
δQ →→ ΔQ=∫ₚₐₜₕδQ, ∮δQ≠0 p.s. ∆指巨觀變化量,由微觀變化量積分而成
δWᵣₑᵥₑᵣₛᵢᵇₗₑ=F∙dx=P∙dV p.s. δ指與路徑有關的微觀變化;d指與路徑無關的微觀狀態變化
Intensive variables: T, P, ρ(g/cm³), Xᵢ(mole fraction) 與mass, size, moles無關的變數
Extensive variables: nᵢ, U, H, S, A, Gdepend on mass, size.
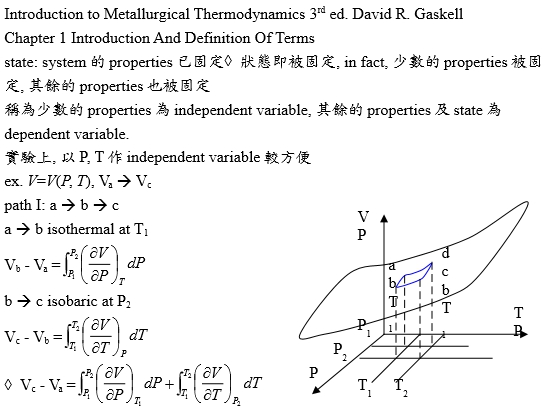
state: system的properties已固定→狀態即被固定, in fact, 少數的properties被固定, 其餘的properties也被固定,稱為少數的properties為independent variable, 其餘的properties及state為dependent variable.
實驗上, 以P, T作independent variable較方便
ex. V=V(P, T), Va → Vc
path I: a → b → c
a → b isothermal at T₁, Vb - Va=∫ᴩ₁ᴾ₂(∂V∕∂P)ᴛ₁dP
b → c isobaric at P₂, Vc - Vb=∫ᴛ₁ᵀ₂(∂V∕∂T)ᴘ₂dT
∴ Vc - Vₐ =∫ᴩ₁ᴾ₂(∂V∕∂P)ᴛ₁dP+∫ᴛ₁ᵀ₂(∂V∕∂T)ᴘ₂dT
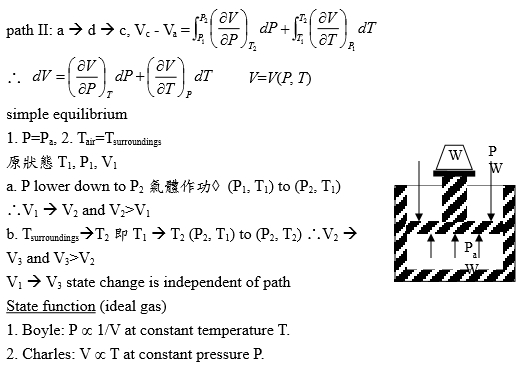
path II: a → d → c, Vc - Va=∫ᴩ₁ᴾ₂(∂V∕∂P)ᴛ₂dP+∫ᴛ₁ᵀ₂(∂V∕∂T)ᴘ₁dT
if ∆Vₚₐₜₕ₋₁=∆Vₚₐₜₕ₋₂, V=V(T, P) state function → dV exact differential
∴dV=(∂V∕∂P)ᴛdP+ (∂V∕∂T)ᴘdT V=V(P, T) i.e. setting M=(∂V∕∂P)ᴛ, N=(∂V∕∂T)ᴘ
相反的, if (∂N∕∂P)ᴛ=(∂M∕∂T)ᴘ → dV exact differential and V=V(T, P) state function
e.g. W=W(x,y,z) → dW=(∂W∕∂x)y,zdx+(∂W∕∂y)x,z dy+(∂W∕∂z)x,y dz
setting (∂W∕∂x)y,z=X, (∂W∕∂y)x,z=Y, (∂W∕∂z)x,y=Z
if ∂X∕∂y=∂Y∕∂x, ∂Y∕∂z=∂Z∕∂y, ∂X∕∂z=∂Z∕∂x → dW exact differential and W=W(x,y,z) state function.
Appendix B ex.-1 verify W=x²y³+xzstate function or not?
state function Z(x,y): state 1 →→ state 2 , ∆Z=Z₂-Z₁=∫₁²dz
dz=(∂Z∕∂x)ydx+(∂Z∕∂y)xdy=Mdx+Ndy i.e. x, y 是自變數
Eq. of State (ideal gas) V=V(T,P)=?
1. Boyle: P ~ 1/V at constant temperature T. If P₀ → P, P₀V(T,P₀)=PV(T,P)....(1)
2. Charles: V ~ T at constant pressure P. If T₀ → T, V(T₀,P₀)/T₀=V(T,P₀)/T....(2)
(2)代入(1), P₀(T/T₀)∙V(T₀,P₀)=PV(T,P)→P₀∙V(T₀,P₀)/T₀=PV(T,P)/ T=c₀ ⸫P₀∙V₀/T₀=P∙V/T
Avogadros hypothsis: “g-mole” ideal gas at T=0℃, P=1 atm, its volume=22.4l
Gas constant, R=(1atm∙22.4l)/(273K∙mole)=0.082057(atm∙l/K∙mole)=8.314J/moleK=1.987 cal/K•mole
∴ Equation of state PV=RT 一莫耳理想氣體方程式or PV=nRT i.e. V=V/n
molar quantity: V, U....(intensive)
work units
1 atm=1.0132×105 Nt/m2≈ 105 Pa=1013 hPa(百帕) 1 l×1 atm=1.0132×102 J
*temperature scale: H₂O ice point: 0℃ 32℉
boiling: 100℃ 212℉
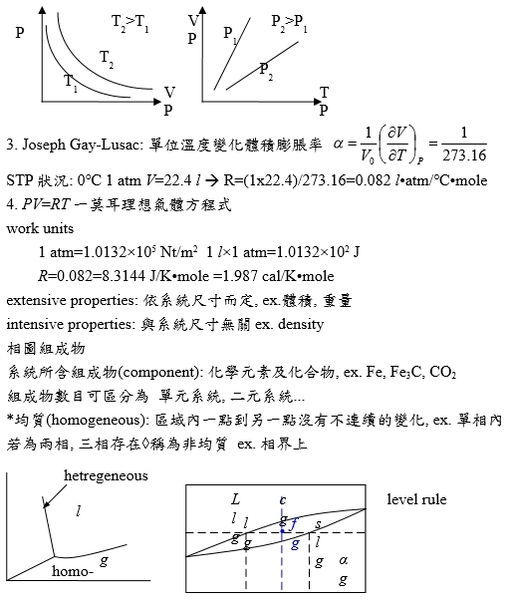
1802 Louis & Lussac 發現永久氣體熱膨脹係數 α=1/V∙(∂V∕∂T)ᴘ=c=1/273.16
相圖組成物
系統所含組成物(component): 化學元素及化合物, ex. Fe, Fe3C, CO2
組成物數目可區分為 單元系統, 二元系統...
*均質(homogeneous): 區域內一點到另一點沒有不連續的變化, ex. 單相內
若為兩相, 三相存在稱為非均質 ex. 相界上