Chap. 1 crystal structure
Crystal structure: an ideal crystal is constructed by an infinite repeatition in space of identical structure units.
Lattice—點之間的關係
r=r+u₁a₁+u₂a₂+u₃a₃… (a) u1,u2,u3 are integrals
Crystal lattice={lattice point}={r|r=r+u₁a₁+u₂a₂+u₃a₃}
-
primitive axes—a₁, a₂, a₃ primitive translational vector, any two points 之間rr滿足(a).
-
Primitive cell—the parallepiped defined by primitive axesa₁, a₂, a₃ is called a primitive cell. 只有一個lattice point, Vc=|a₁∙a₂a₃|若是primitive cell, 體積是最小的
Another way of choosing a primitive cell: Wigner-Seitz cell
Basis—atom array in a cell
crystal structure=lattice+basis, rj=xja₁+yja₂+zja₃ xj≤1, yj≤1, zj≤1在cell內部
Fundamental types of lattices
Symmetry operators—the symmetry operators of a crystal carry the crystal structure into itself.
-
lattice translation T=u₁a₁+u₂a₂+u₃a₃
-
mirror reflection
-
inversion: r→-r
-
rotation
|
角度限制 |
60 |
90 |
120 |
180 |
360 |
|
對稱性 |
6 fold |
4 |
3 |
2 |
1 |
,2的旋轉,任何lattice均不變
Bravais lattice: 5 2-D and 14 3-D
2-D lattice 用a1,a2, 表示
i) oblique: a1a2, 90, ii) square: a1=a2, =90 iii) hexagonal: a1=a2, =120 iv) rectangular: a1a2, =90, v) centered rectangular: a1a2, =90
3-D lattice用a1,a2,a3,,, 表示7 systen/14 types
-
one fold 對稱, Triclinic a1a2a3, P(1)
-
Monoclinic a1a2a3, ==90 P, C(2)
-
Orthorhombic a1a2a3, ===90 P, C, I, F(4)
-
Tetragonal a1=a2a3, ===90 P, I(2)
-
Cubic a1=a2=a3, ===90 P, I, F(3)
-
Trigonal a1=a2=a3, ==<12090 P(1)
-
Hexagonal a1a2a3, ==90, =120 P(1)
Cubic lattice
-
S.C.(Simple cubic)
-
B.C.C.(Body centered cubic)
-
F.C.C.(Face centered cubic)
Number of nearest neighbors and its distance
(i)S.C.: (6, a) (ii)B.C.C.: (8, √3a/2 ) (iii)F.C.C.: (12, √2a/2 )
Volume of primitive cell
-
S.C.: a3
-
B.C.C.: a₁=½a(i+j-k), a₂=½a(-i+j+k), a₃=½a(i-j+k)
Vₚ=|a₁∙a₂a₃|=(a/2)³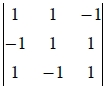 = a³/2
= a³/2
-
F.C.C.: a₁=½a(i+j), a₂=½a(j+k), a₃=½a(i+k) Vₚ=|a₁∙a₂a₃|=(a/2)³
 =a³/2
=a³/2
Packing fraction(p.f.): the maximum proportion of the available volume that an be filled with hard spheres.
-
S.C.: volume of a sphere=4π/3(a/2)³, number of hard sphere in a cubic cell=1, volume of cell=a3. p.f.= [4π/3(a/2)³]/a³=π/6=0.524=52.4%
-
B.C.C.: volume of a sphere=4π/3(√3a/4)³ , number of hard sphere in a cubic cell=2, volume of cell=a3. p.f.= 2[4π/3(√3a/4)³]/a³=√3π/8=0.68=68%
Miller indices: 1/X₁:1/X₂:1/X₃=h:k:lplane’s indices=(h,k,l)
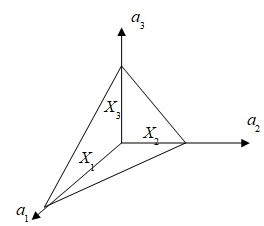
direction: [u,v,w]=ua1+va2+wa3
* only in cubic system, [h,k,l](h,k,l)
{1,0,0} includes (1,0,0), (-1,0,0), (0,1,0), (0,-1,0), (0,0,1), (0,0,-1)
Simple crystal structure
-
NaCl structure: crystal structure=lattice + basis, space lattice: F.C.C. and basis: two atoms. Cl- :(0,0,0), Na+:(½, ½, ½)
-
CsCl structure: space lattice: S.C. and basis: two atoms. Cs+:(0,0,0), Cl-:(½, ½, ½)
-
hexagonal close-paced structure has maximum packing factor.
-
Diamond: space lattice: F.C.C.(兩個F.C.C.交錯) and basis: two atoms. (0,0,0), (¼,¼,¼), 4 neighbor atoms.
In cubic system, the direction[h,k,l] is perpendicular to (h,k,l)
A=ha₁+ka₂+la₃, AB=0B-0A=a₂/k-a₃/h, AC=0C-0A=a₃/l-a₁/h,
N=ACAB=(1/hkl)[la₁a₂+ka₃a₁+ha₂a₃]
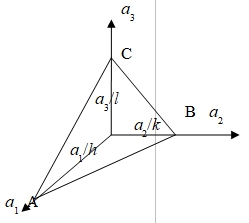
欲[h,k,l]plane(h,k,l) → N // A
m(a₂a₃)=a₁, n(a₃a₁)=a₂, p(a₁a₂)=a₃
a₁∙a₂=0, a₁∙a₃=0 ⸫ a₁, a₂, a₃ is orthorgonal.
a₁=m(a₂a₃)=m(a₂a₃/a₁)a₁ → m=a₁/a₂a₃, n=a₂/a₁a₃, p=a₃/a₁a₂ N=nA, nR N=(1/hkl)[l(a₁a₂/a₃)a₃+k(a₁a₃/a₂)a₂+h(a₂a₃/a₁)a₁] → h:k:l=h(a₂a₃/a₁):k(a₁a₃/a₂):l(a₁a₂/a₃)
tell us a₂a₃/a₁=a₁a₃/a₂=a₁a₂/a₃ → a1=a2=a3
所以cubic system a1=a2=a3, ===90, [h,k,l](h,k,l)


