牙科門診靜脈鎮靜病患之口咽累積水量會增加咳嗽-J Oral Rehabil,2008
2011/06/16 12:55
瀏覽771
迴響0
推薦0
引用0
Accumulated oropharyngeal water increases coughing during dental treatment with intravenous sedation.
Kohjitani A, Egusa M, Shimada M, Miyawaki T. J Oral Rehabil. 2008 Mar;35(3):203-8.
Department of Dental Anesthesiology, Okayama University Hospital of Medicine and Dentistry, Okayama, Japan. atsushik@denta.hal.kagoshima-u.ac.jp
Abstract
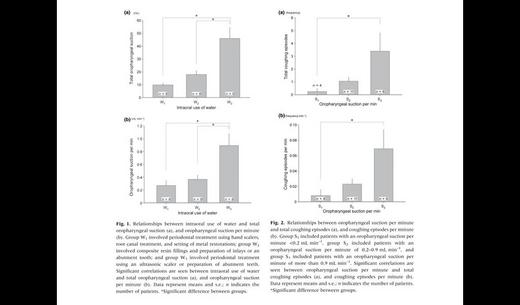
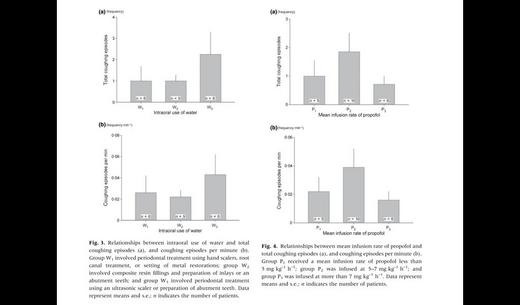
In dental procedures performed under intravenous sedation in patients with intellectual disabilities, procedures are sometimes interrupted by the cough reflex, which may be triggered by intraoral use of water and/or increased secretion stimulating the pharyngeal/laryngeal mucosa, or by those irritating the tracheal mucosa directly through anesthetics-induced impairment of the laryngeal closure reflex. We investigated relationships between frequency of coughing episodes and intraoral use of water, water remaining in the oropharyngeal space, and mean infusion rate of propofol during dental treatments performed under intravenous sedation with midazolam and propofol. Twenty-one intellectually disabled patients were enrolled. After induction, a 14 Fr. suction catheter was inserted nasally, which was fixed where oropharyngeal suction could be done most effectively. Patients were divided into three groups according to the amount of intraoral use of water, amount of oropharyngeal suction and mean infusion rate of propofol. The amount of oropharyngeal suction significantly correlated with intraoral use of water. Frequency of coughing episodes significantly correlated with amount of oropharyngeal suction per minute. However, coughing episodes correlated neither with intraoral use of water nor with infusion rate of propofol. These findings suggested that accumulation of water in the oropharynx increased vulnerability to the cough reflex in dental treatments performed under intravenous sedation.
部份內文翻譯:
- 吞嚥與咳嗽反射可以清除喉部與上呼吸道過多的唾液、分泌物或外來物體(如食物),它們是重要的呼吸道保護機制。吞嚥是防止分泌物或外來外物質進入呼吸道的最重要反射,咳嗽則是可能發自自主行為或是作為反射的一部份。
- 牙科門診治療時發生的咳嗽,會誘發暫時性的聲門關閉,進而導致血氧下降。腦部功能的缺損(好比腦性麻痺、服用嗎啡類藥物)會抑制咳嗽反應,以致於這類病患易因口內外來物質的增加而入侵其呼吸道。是以,適度地保留此一保護性反射,是在牙科門診(鎮靜)治療過程中必要的工作。
- 靜脈鎮靜已普遍地被應用在牙科門診診療,但是,咽喉黏膜仍可能受到口內(冷卻)沖水或漸增的分泌物(口水)的刺激;或是麻醉/鎮靜藥物作用造成喉部閉合反射的受損,使得前述物質得以直接刺激氣管黏膜,誘發咳嗽反射,進而中斷牙科診療步驟。
- 21名17歲至61歲特殊需求病患,其中16名為心智發展障礙,4名心智發展障礙合併自閉症,以及1名病毒性腦膜炎後失智症病患。鎮靜/麻醉前六小時內不得吃固體食物,三小時內不得飲用無顆粒飲料。由靜脈導管給予2~4 mg midazolam和20 mg propofol,接著再以4~9 mg/kg/h輸注propofol,並維持病患自發性呼吸-鼻管氧氣為2 L/min。以Ramsay評級作為鎮靜深度指標,調控propofol注輸速率使鎮靜深度維持在4至5之間(Dr. Fan按:相當於OAA/S分級第2至3間)。呼吸道藉由側頭/歪頭、提下巴/頷頦、置入人工鼻管呼吸道等措施,以避免上會厭(supraglottic)呼吸道發生阻塞。鎮靜誘導後,將接上真空抽吸機的14 Fr導管(SAFEED suction catheter),經鼻道置入10-15公分至咽部位置,其頂端多居於軟顎下緣(below the inferior margin of the soft palate)0-2公分,以利抽吸。
- 量測變項包括:口內注入水量和口咽抽吸水量、咳嗽頻率和口內注入水量、咳嗽頻率和每分鐘口咽抽吸水量、咳嗽頻率和平均propofol注輸速率。診療內容分成三類:(1)有六位病患接受使用手用刮牙器治療牙周組織、根管治療和金屬補綴/填補-甚少沖水,(2)有九位病患接受複合樹脂填補和製備多個鑲嵌體或單顆橋基牙,(3)有六位病患接受超音波刮牙器治療牙周組織、製備多顆橋基牙/支台齒-需大量沖水。為便利統計分析,口內抽水量亦分成三組,(1)口咽抽吸水量小於0.2 ml/分(計4名),(2)口咽抽吸水量介於0.2~0.7 ml/分(計11名),(3)口咽抽吸水量大於0.7 ml/分(計6名)。
- 統計分析:Speraman's分級相關係數(Spearman's correlation coefficient by rank)檢視口內沖水量、口咽抽吸水量、咳嗽次數和propofol平均注輸速率間之關係。同時以單因子變異數分析(one-way ANOVA)暨Bonferroni進行事後多重檢定較正(Bonferroni post-hoc multiple comparisons),檢定組間之統計顯著性,p < 0.05為具顯著差異。
- 初步結果:(1)咳嗽總次數或每分鐘咳嗽次數與每分鐘口內抽吸水量分組(三組),具明顯正相關,(2)因應診療內容的口內沖水量(三類),各組間之咳嗽總次數或每分鐘咳嗽次數無明顯差異。
- Ramsay sedation scale
- Anxious or restless or both
- Cooperative, orientated and tranquil
- Responding to commands
- Brisk response to stimulus
- Sluggish response to stimulus
- N o response to stimulus
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 |
自訂分類:牙科門診鎮靜-專業版
你可能會有興趣的文章:
限會員,要發表迴響,請先登入