

台灣同胞與有榮焉,祖國強大的太空科技將服務予全體海內外的中國人,因此部份島內偏激搞台灣獨立的團體與個人,因當修正自己僵化頑劣的思想,親美哈日的日子已經到底限,被利用而犧牲掉是美國的陰謀,傳聞台灣當局限制新聞媒體報導中國成功發射太空船並且建造太空站的訊息? 實屬不當的舉措.
看中華民族的驕傲與光榮,這是全體中國人的努力以赴的成果,21世紀太空競賽爭霸戰,中國來臨.嫦娥姐姐請從月球的廣寒宮移居到中國太空站,那裡有美味可口的家鄉菜,也有熱水沐浴,看電視節目,打電動遊戲,最難能可貴是有視訊影視通訊系統,可以即時與丈夫后羿通訊解決相思病.
2025年中國將登陸月球為妳建造新的廣寒宮敬請期待.


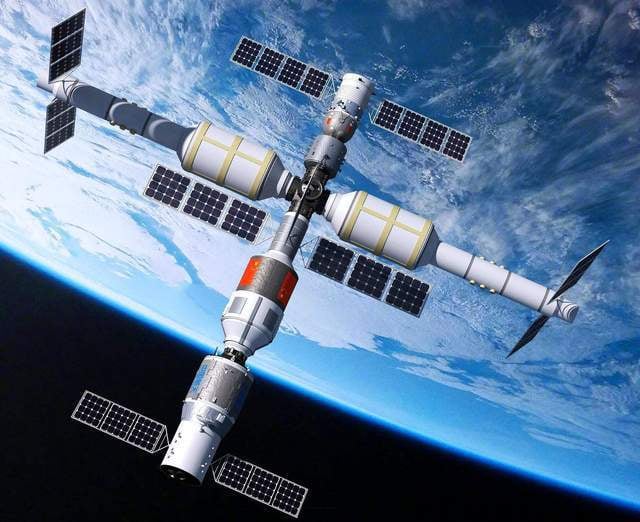
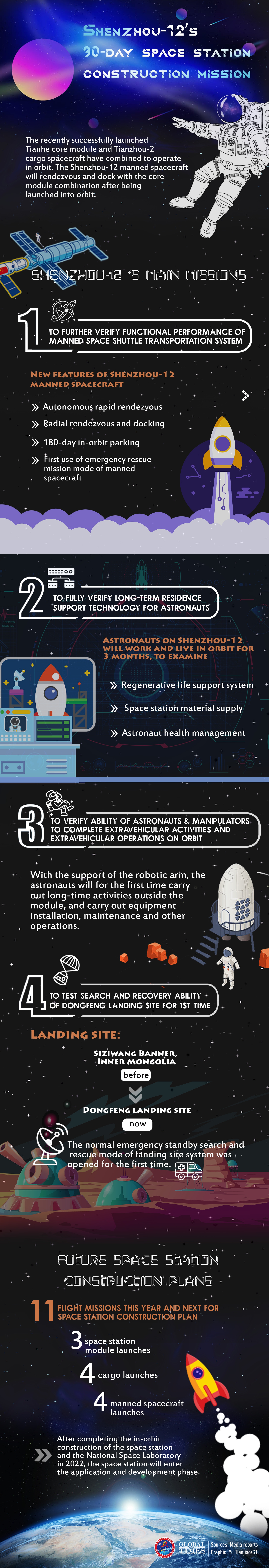
中國長征五號B火箭運載著「天和號」核心艙,在20210429日順利於海南文昌發射中心升空,並順利抵達軌道,正式拉開中國建設太空站的序幕。
中國太空站的基本結構分為3個艙體天和核心艙、問天實驗艙、夢天實驗艙。天和號是空間站的骨幹,也是第一個發射入軌的艙體,它同時是中國目前自主研製的規模最大、系統最複雜的太空艙。其他艙體將在不同時間發射入軌並組裝,預計中國太空站整體將於2022年底全面營運。.......................
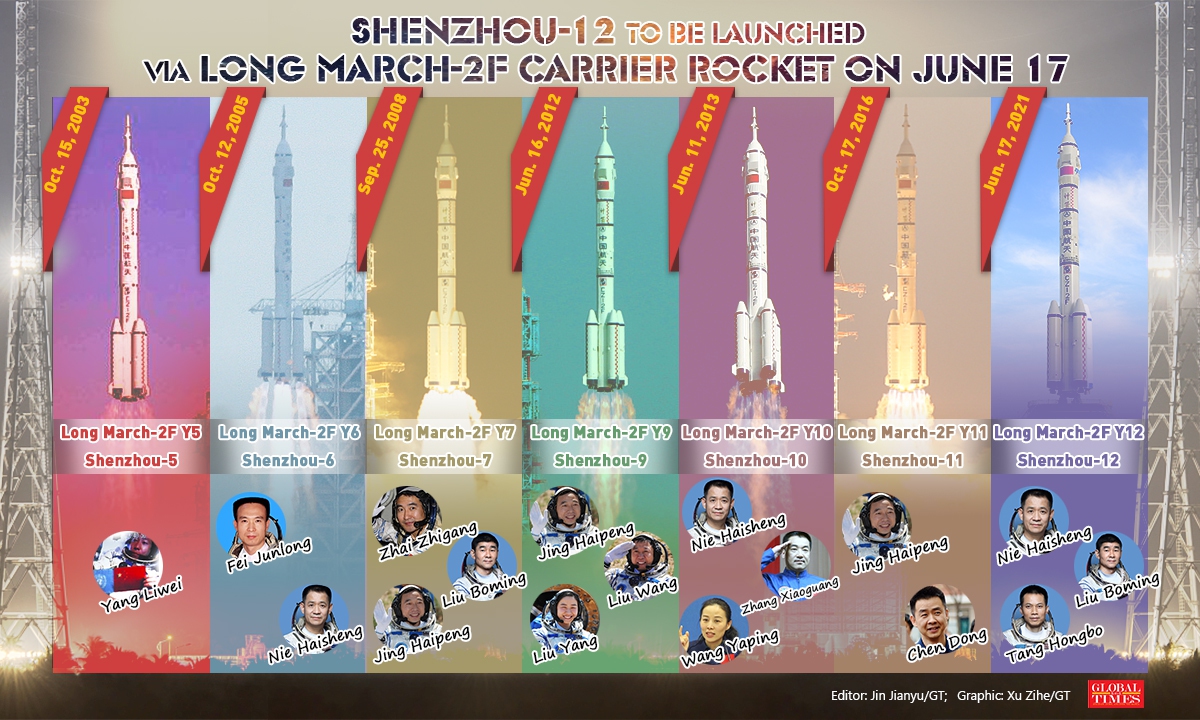
The Shenzhou-12 mission is the first crewed mission by the Chinese space program in five years and the seventh overall mission of the Shenzhou spacecraft, which conducted its first crewed flight in 2003. For comparison, the seventh U.S. crewed spaceflight was Gemini 3 in 1965, the first flight of the new two seat spacecraft commanded by Gus Grissom, with John Young as the pilot. The seventh Soviet crewed spaceflight was Voskhod 1 in 1964 which flew three cosmonauts in a spacecraft based on the Vostok but with modifications and the ability to fly multiple crewmembers.
Each crewed Shenzhou mission to date has featured new milestones in Chinese human spaceflight, but Shenzhou-12 is inteded to start an improved cadence of Chinese human spaceflight launches, being the third of 11 missions in the 2021-2022 timeframe to build up the new Chinese space station.
The first mission in this series was the launch of Tianhe in April. The next was the launch of Tianzhou-2 late last month. The Tianzhou is a robotic cargo spacecraft based on the Tiangong-1 mini space station, and fulfills a similar role to the Chinese program that Progress and Cygnus fulfill for ISS.
The Tianzhou-2 cargo ship was filled with supplies for the Shenzhou-12 crew and had to dock successfully to Tianhe before the Shenzhou mission could go ahead this month.The Shenzhou-12 mission will be followed by the Tianzhou-3 robotic cargo flight in September and the Shenzhou-13 crew mission in October, making 2021 the first year with multiple Chinese crewed launches. For 2022, the Chinese space station flight manifest features the Tianzhou-4 and Shenzhou-14 flights in the spring, the Tianzhou-5 and Shenzhou-15 flights in the fall, and the Wentian and Mengtian scientific modules set for summer launches.
The Shenzhou-12 mission is planned to dock with the Tianhe space station core module as early as six hours after liftoff, though the actual docking time is not yet known. The crew members will enter the station and outfit it for their three-month mission. They will no doubt find the core module, with a living space of 50 cubic meters, roomier than the Shenzhou spacecraft they launched on.
The Tianhe core module, like the Mir core module and ISS Zvezda module, features six docking ports and a robotic crane to move future additional modules to their correct docking ports. The Wentian and Mengtian science modules will have most of the equipment and capability needed for science and spacewalks, but the Tianhe module will have some experiment capability for the Shenzhou-12 and 13 mission crewmembers to use.
The Tianhe’s main function is as a control center and living quarters for the station, and the Shenzhou-12 crew will be the first to use the living quarters as well as the control systems. The Shenzhou-12 crew is also planned to conduct two spacewalks during their mission.
The Shenzhou-12 crew is expected to be the first of many to reside aboard the Chinese Space Station, and not all occupants are expected to be Chinese. Russia has announced that it will fly Soyuz spacecraft and crews to the Chinese station from Vostochny or Kourou, and the European Space Agency has an agreement with the Chinese space agency CNSA as well for its astronauts and research to use the Chinese station.
China has also signed an agreement with the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs to allow the Chinese station to host international experiments, and some of these experiments have already been chosen. In the future, this cooperation could extend to hosting astronauts from developing countries without their own program, along with ESA and Russian crewmembers.
ESA astronauts Matthias Maurer and Samantha Cristoforetti have trained with the Chinese program and its taikonauts, as part of preparations for a future cooperative spaceflight. As ESA astronaut Maurer stated, “I am very much looking forward to expanding our cooperation with our Chinese friends into space.”
The Chinese Space Station is also planned to host a Hubble Space Telescope-class orbiting astronomical observatory known as Xuntian, scheduled for launch in 2024. This observatory would fly free in its own orbit to conduct observations and would dock with the station periodically for servicing.
The Shenzhou-12 mission is another step in China’s plans to become a increasingly prominent spacefaring power. These plans will expand the number of humans in space and are expected include plans for a crewed landing on the Moon sometime in the next 10-15 years.
浩瀚無垠的太空咱們中國人前來報道敬請多多關造謝謝.
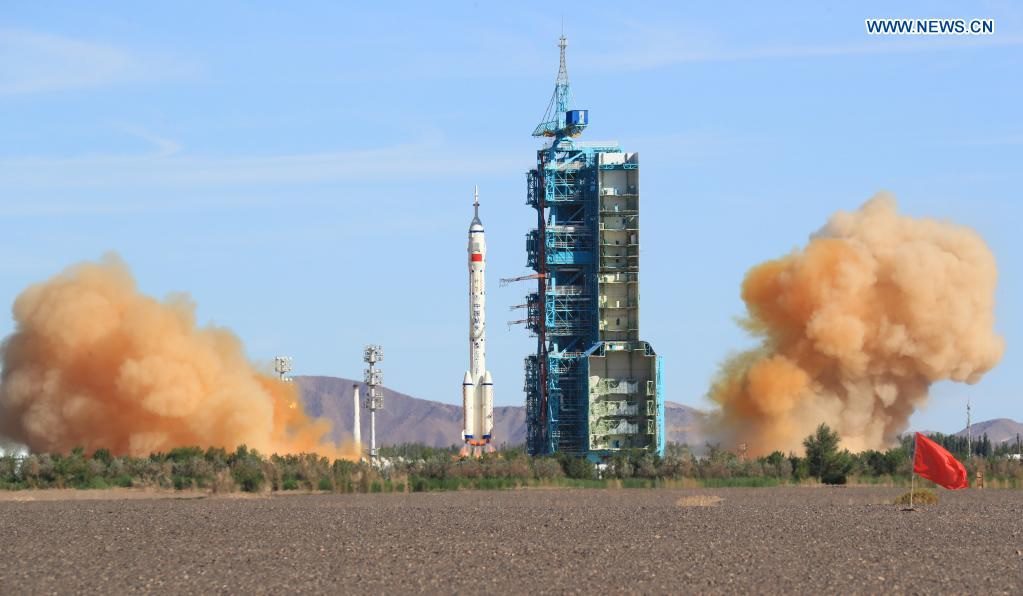
Space, here we come! China is set to launch the Shenzhou-12 manned spacecraft to ferry three astronauts, including two veteran astronauts, to its Tianhe space station core module at 9:22 am on Thursday, Global Times learned from the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA) ..
According to the agency, astronauts to ride Shenzhou-12--Divine Vessel in Chinese - are Nie Haisheng, Liu Boming and Tang Hongbo, and the three made their public appearance prior to the launch at Wentian Pavilion in the Jiuquan Satellite Space Center, located in the Gobi Desert in Southwest Chinas Gansu Province on Wednesday during a press event.
20210617 日上午 9 點 22 分,3 名中國太空人湯洪波,聶海勝,劉伯明搭乘神舟 12 號太空船,藉長征二號 F 運載火箭順利升空並預計 17 日下午與太空站對接,他們將在軌道上停留 3 個月,測試太空站生命支持系統。
這樣一來是中華民族的驕傲與光榮,雖然晚於蘇聯及美國的太空站,中國人終於實現建設屬於自己的太空站,中國獨立自主研究,開發,設計,製造的太空船與太空實驗站,雖然晚於西方國家35年但是屬於最新的太空站...
長征二號 F 運載火箭(簡稱長二 F,別稱「神箭」,縮寫 CZ-2F 或 LM-2F)自中國酒泉衛星發射中心升空,上面搭載了該國神舟 12 號載人飛船(Shenzhou-12)上午 9 時 43 分左右,中國宣布此次任務圓滿成功,按照行程表,神舟 12 號飛船 17 日下午就會與太空站對接。3 名中國太空人將在這裡度過 3 個月,太空船內有各自獨立的休息空間,一台跑步機和通訊中心,其中 2 名太空人為了接下來多次模塊對接任務,將展開 2 次太空行走於艙外維護系統。
.
Shenzhou-12 and three crew members successfully launch to new Chinese space station.
The first crewed mission to the new Chinese Space Station has successfully launched. Shenzhou-12, carrying three taikonauts, lifted off on Thursday June 17 at 01:22 UTC from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in the Gobi Desert in northwest China.
Shenzhou-12 launched on top of the human-rated Long March 2F vehicle, which is based on the retired Long March 2E rocket formerly used to launch geostationary satellites. Also known as the Chang Zheng 2F (CZ-2F), the launcher is equipped with two stages and four liquid rocket boosters, all fueled by nitrogen tetroxide and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH).
These hypergolic fuels are very toxic, which would become a significant problem if the rocket’s remains were to impact a populated area. Future Chinese launch vehicles are being designed to avoid using these propellants.
The vehicle is also equipped with a Soyuz-style fairing, with grid fins and a solid-fueled escape motor on top, to ensure that the crew would be able to escape a failing booster. This technology is based on the abort system used on the Soyuz carrier rocket, which has been used a few times over the years to save flight crews, most recently the Soyuz MS-10 crew in October 2018.
Like the abort system, the Shenzhou spacecraft that will be flying to the new Chinese space station this week draws heavily on Soyuz technology. Shenzhou was approved in 1992 as part of the Chinese human spaceflight initiative known as Project 921, and has a design layout very similar to the long-serving Soyuz spacecraft built in Russia.

 ...
...
In the front of the spacecraft, the orbital module for Shenzhou-12 and future spacecraft contains an androgynous docking ring based on Russian APAS technology (used on ISS), which will be used to dock to the Tianhe core module. In the middle, the descent module containing the crew is a scaled-up version of the Soyuz descent module with a very similar mold line. The rear of the spacecraft is a service module equipped with engines, fuel tanks, and solar panels, much like the Soyuz and Progress spacecraft.
The mission will be commanded by Nie Haisheng, who is making his third spaceflight. He has previously flown on the Shenzhou-6 and Shenzhou-10 missions, the latter flying to the Tiangong-1 space station in 2013. Nie, from Hubei province, is 56 years old and is a major general in the People’s Liberation Army Air Force (PLAAF). At the end of this mission, he will have spent approximately 114 days in space, becoming the all-time Chinese record holder for the longest time total in space.
Nie is accompanied by two crew members, referred to as “operators.” The first Shenzhou-12 operator is Liu Boming, 54, from Heilongjiang, who previously flew on Shenzhou-7 in 2008 and became a participant in China’s first ever spacewalk. The second is Tang Hongbo, who like Liu, is also a PLAAF fighter pilot. Both crewmembers and their commander will stay on board the new space station for approximately 90 days before coming home in September.
The three crew members, wearing launch and entry suits based on a reverse-engineered Sokol suit provided by Russia, will walk out past military officers and a crowd of well-wishers and board a bus to the launch pad. After boarding the Shenzhou descent module crew compartment, they’ll launch on a 41 degree inclination relativie to the equator, into an orbit that will end up 370 kilometers in altitude to rendezvous with the Tianhe space station core module.
















