北京時間2018年12月27日,北斗三號正式提供全球服務。
20181227,中國衛星導航系統管理辦公室主北斗衛星導航系統宣佈北斗三號基本系統完成建設,於27日開始提供全球服務。這標誌著北斗系統服務範圍由區域擴展為全球,北斗系統正式邁入全球時代。
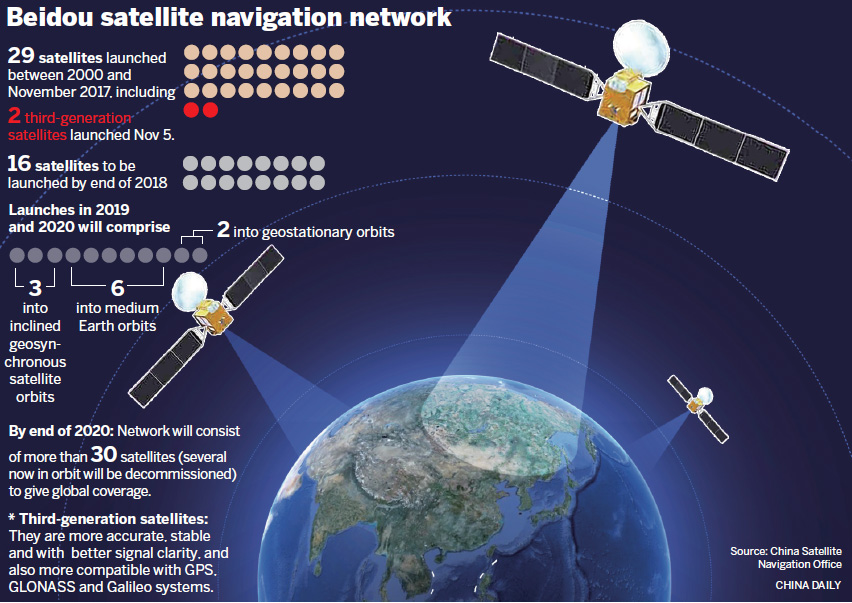
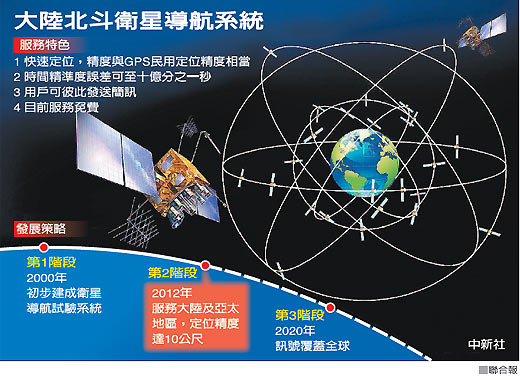
美國和歐洲都迅速作出了反應,美國認為, 「北斗」的服務類似GPS,利用一系列衛星為用戶提供誤差約10米的精確定位。全球銷售的大多數智慧型手機晶片都將與北斗系統相容,目標是在未來成為主導技術。根據計劃,到2020年中國將繼續發射11顆北斗三號和1顆北斗二號衛星,數量將增至44顆;2035年建成以北斗為核心,更加泛在、更加融合、更加智慧的綜合定位導航授時(PNT)體系。
美國認為中國「北斗」對GPS的挑戰也屬於「威脅」一部份,消除這種威脅有兩種手段:
一,美國利用自身強大的國力,強行施壓,迫使中國放緩包括「北斗」系統在內的太空計劃進程。
二,美國加大人力,財力,物力投入,保持領先地位。商業上,中國安全高效而且極具價格優勢的衛星, 直接威脅波音等美國公司在世界衛星通信市場的商業利益和地位。
「北斗」系統建成的意義遠不止於商業。GPS儘管免費,但可以讓各國處於依賴地位。只開放「民碼」,精確度與「軍碼」相差幾十倍。一旦某大國與美國進入極端關係時期,「民碼」一停或提供「偽碼」,對手就無法有效使用衛星制導飛彈。
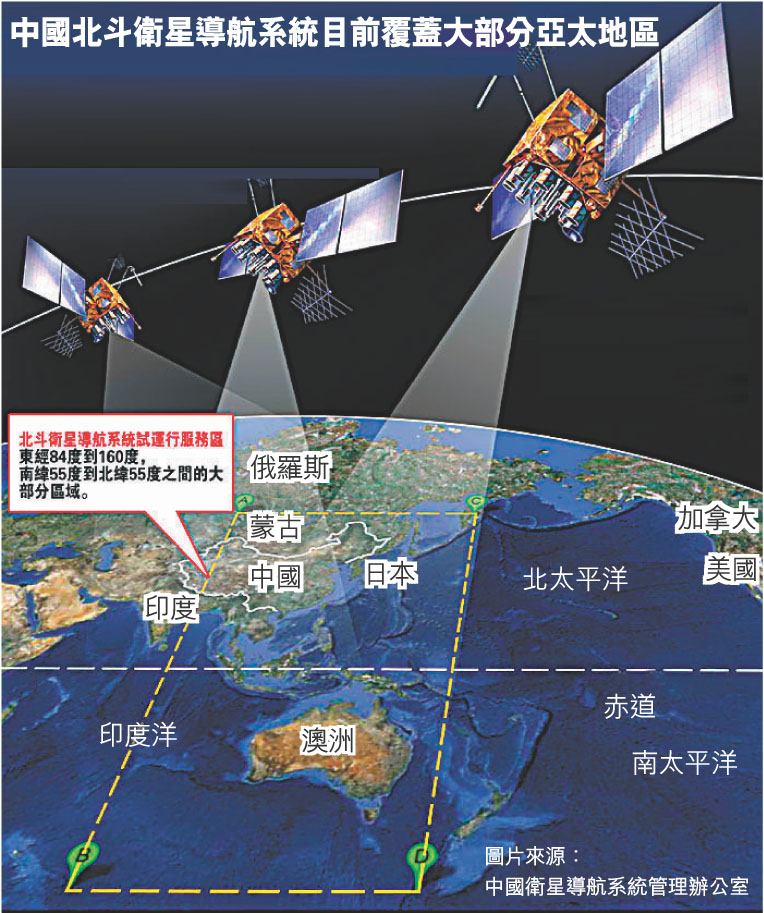
北斗衛星導航系統(:Beidou Navigation Satellite System,簡稱BDS)是中華人民共和國獨立自主建設的一個衛星導航系統],北斗衛星導航系統由兩個獨立的部封包成,一個是2000年開始運作的區域實驗系統,另一個是已經開始面向全球服務的全球導航系統。
北斗衛星導航系統(BDS)、美國全球定位系統(GPS)、俄羅斯全球導航衛星系統(GLONASS)和歐盟伽利略定位系統(Galileo)為聯合國衛星導航委員會認定的全球衛星導航系統四大核心供應商[]。
2018年11月,已發射了19顆第三代在軌導航衛星。按照計劃,該系統將在2018年覆蓋「一帶一路」國家,2020年完成建設提供全球定位服務,2035年建成以北斗為核心的綜合定位、導航、授時體系。
The BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) běi dǒu wèi xīng dǎo háng xì tǒng [pèi tòu wêi ɕíŋ tàu xǎŋ ɕî tʰʊ̀ŋ]) is a Chinese satellite navigation system. It consists of two separate satellite constellations. The first BeiDou system, officially called the BeiDou Satellite Navigation Experimental System and also known as BeiDou-1, consists of three satellites which since 2000 has offered limited coverage and navigation services, mainly for users in China and neighboring regions. Beidou-1 was decommissioned at the end of 2012.
The second generation of the system, officially called the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) and also known as COMPASS or BeiDou-2, became operational in China in December 2011 with a partial constellation of 10 satellites in orbit.] Since December 2012, it has been offering services to customers in the Asia-Pacific region.] On December 27, 2018, Beidou-3 officially began to provide global services.[
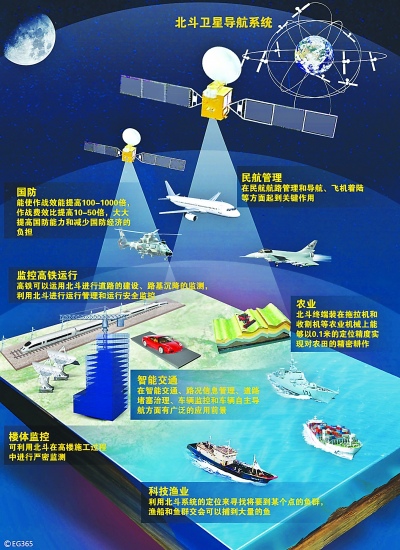
中國北斗衛星導航系統(:Beidou Navigation Satellite System,簡稱BDS.提供飛機輪船汽車各式各樣交通運輸工具更有效更精密正確的衛星定位服務與通訊使用在重大災難發生時更加精准判定受災區域及立體圖像資料傳遞以利救災行動進行.預計2020年以後中國生產的汽車飛機輪船等交通工具將裝設標準BDS系統使用至於台灣地區亦步亦趨一視同仁可選擇服務使用中國BDS或是美國GPS.
The Beidou-3M/G/I satellites represent the orbital segment of the third phase of the Chinese Beidou navigation system which uses satellites in Medium Earth Orbit and Geosynchronous Orbit and is also known as the Compass Navigation Satellite System.
Beidou is already in operation for the Chinese and Asia-Pacific Area with global availability planned by 2020 when all satellites will have been launched. The China Satellite Navigation Project Center is in charge of program management.
The concept for a Chinese Navigation System was first presented in 1983. In 1989, two hosted payloads confirmed the feasibility of operating a dual-satellite regional navigation system from Geostationary Orbit. Beidou was approved as a program in 1993 to provide China with independent access to regional and global navigation, no longer relying on foreign systems like the American GPS and Russian Glonass System. Beidou is the Chinese name of the Big Dipper constellation which was used in ancient navigation to locate the North Star.
The Beidou Global Navigation system was outlined for a step-wise implementation starting with an experimental system consisting of three satellites in Geostationary Orbit, located above the Chinese territory to provide local navigation services. The second phase of the project is the deployment of operational Beidou navigation satellites to initially establish a regional navigation system before expanding to global coverage, going through different satellite modifications to keep up with technical standards. In 2020, full global Beidou coverage will be achieved.